SentinelResource的fallback属性
fallback属性
**概念:**fallback 函数名称,可选项,用于在抛出异常的时候提供 fallback 处理逻辑。fallback 函数可以针对所有类型的异常(除了 exceptionsToIgnore 里面排除掉的异常类型)进行处理。fallback 函数签名和位置要求:
- 返回值类型必须与原函数返回值类型一致;
- 方法参数列表需要和原函数一致,或者可以额外多一个
Throwable 类型的参数用于接收对应的异常。
- fallback 函数默认需要和原方法在同一个类中。若希望使用其他类的函数,则可以指定
fallbackClass 为对应的类的 Class 对象,注意对应的函数必需为 static 函数,否则无法解析。
其实通过官网上提供的概念,我们不难看出这个属性类似于blockHandler,但是各位一定要注意他们有本质的不同。
**注意:**fallback属性和blockHandler属性的本质不同在于他们作用的异常不同:
- blockHandler:针对违反Sentinel控制台配置规则时触发BlockException异常时对应处理的属性
- fallback:针对Java本身出现的异常进行处理的对应属性。
案例演示
上节课我们已经完成环境的搭建,那我们就直接在8084项目的DemoController中编写对应代码
首先我们先来设置异常规则
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| package com.mashibing.cloudalibabaconsumer8084;
import com.mashibing.cloudalibabacommons.entity.JsonResult;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class DemoController {
@Value("${service-url.nacos-user-service}")
private String SERVICE_URL;
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@GetMapping("/consumer/fallback/{id}")
public JsonResult<String> fallback(@PathVariable Long id){
if(id<=3){
JsonResult<String> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL+"/info/"+id,JsonResult.class);
System.err.println(result.getData());
return result;
}else{
throw new NullPointerException("没有对应的数据记录");
}
}
}
|
此时我们任务添加了异常,此时如果我们访问http://localhost:8084/consumer/fallback/4(id非法)地址时,就会出现对应的显示效果:
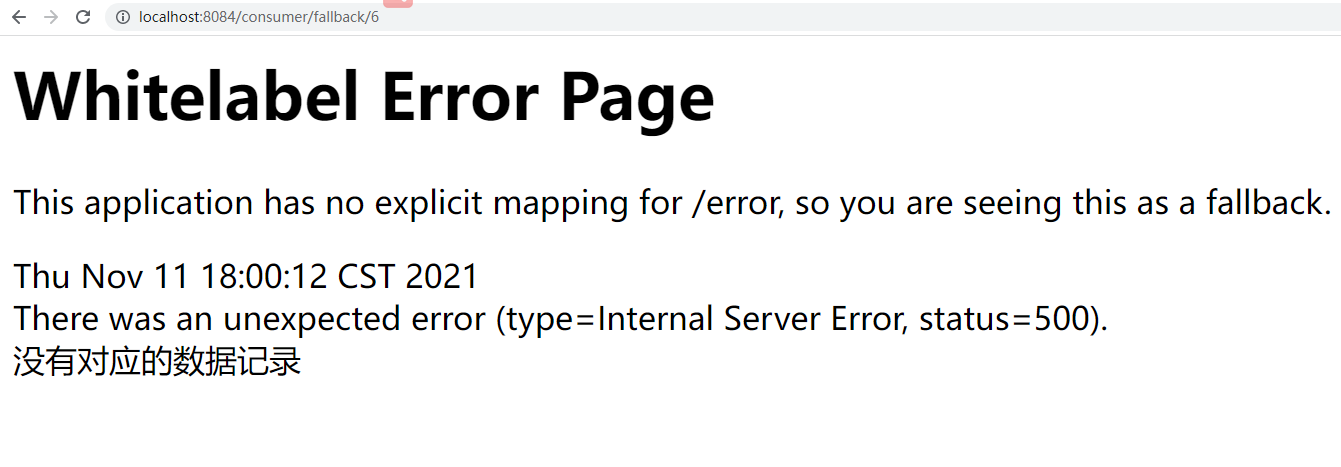
明显此时显示效果非常不好,我们就可以通过@SentinelResource注解的fallback属性来解决这种java异常,给出友好提示
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| @RestController
@Slf4j
public class DemoController {
@Value("${service-url.nacos-user-service}")
private String SERVICE_URL;
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@GetMapping("/consumer/fallback/{id}")
@SentinelResource(value = "falllback",fallback = "fallbackHandler")
public JsonResult<String> fallback(@PathVariable Long id){
if(id<=3){
JsonResult<String> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL+"/info/"+id,JsonResult.class);
System.err.println(result.getData());
return result;
}else{
throw new NullPointerException("没有对应的数据记录");
}
}
public JsonResult<String> fallbackHandler(Long id,Throwable e){
JsonResult<String> result = new JsonResult<>(444,"出现未知商品id");
return result;
}
}
|
到这里为止,我们就很清楚的知道了fallback属性的作用,同时它和blockHandler属性类似,也可以设置fallbackClass属性,来指定对应类型,来处理对应的Java异常,当然要注意和blockHandlerClass属性一样,也需要让所有的方法都必需为 static 函数,否则无法解析。
同时配置blockHandler和fallback属性
通过上述的内容,我们很清楚的知道了fallback属性的作用,但是大家现在想一个问题,如果我们在使用@SentinelResource属性的时候,同时设置blockHandler属性和fallback属性时,并且同时出现了Sentinel异常和Java异常,这个时候会执行哪个方法那。
我们还是回顾一下blockHandler属性的概念:
blockHandler / blockHandlerClass: blockHandler 对应处理 BlockException 的函数名称,可选项。blockHandler 函数访问范围需要是 public,返回类型需要与原方法相匹配,参数类型需要和原方法相匹配并且最后加一个额外的参数,类型为 BlockException。blockHandler 函数默认需要和原方法在同一个类中。若希望使用其他类的函数,则可以指定 blockHandlerClass 为对应的类的 Class 对象,注意对应的函数必需为 static 函数,否则无法解析。
案例演示
我们现在同时在DemoController中设置fallback属性和blockHandler属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| @RestController
@Slf4j
public class DemoController {
@Value("${service-url.nacos-user-service}")
private String SERVICE_URL;
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@GetMapping("/consumer/fallback/{id}")
@SentinelResource(value = "falllback",fallback = "fallbackHandler",blockHandler = "blockHandler")
public JsonResult<String> fallback(@PathVariable Long id){
if(id<=3){
JsonResult<String> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL+"/info/"+id,JsonResult.class);
System.err.println(result.getData());
return result;
}else{
throw new NullPointerException("没有对应的数据记录");
}
}
public JsonResult<String> fallbackHandler(Long id,Throwable e){
JsonResult<String> result = new JsonResult<>(444,"NullPointerException异常");
return result;
}
public JsonResult<String> blockHandler(Long id, BlockException e){
JsonResult<String> result = new JsonResult<>(445,"BlockException限流");
return result;
}
}
|
此时我们来设置Sentinel配置,我们通过熔断规则中的异常数来演示(当然也可以用其他的)
规则:在一秒内超过最小访问次数5次,并且异常数超过2的时候,就会触发熔断规则。
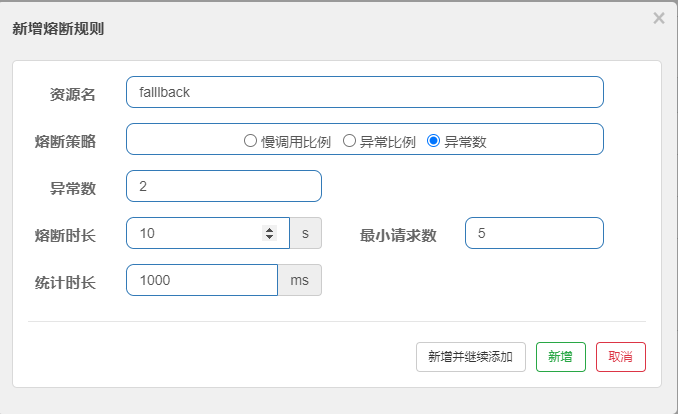
此时我们来访问http://localhost:8084/consumer/fallback/6看效果:
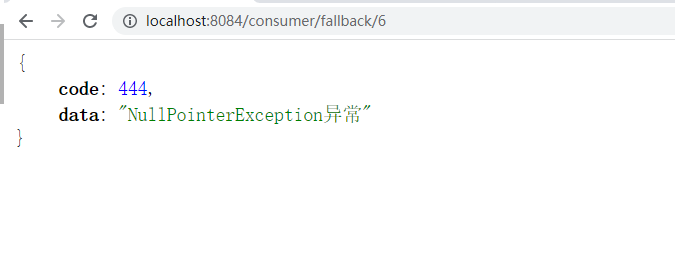
- 在没有触发熔断之前的异常交给fallback来处理
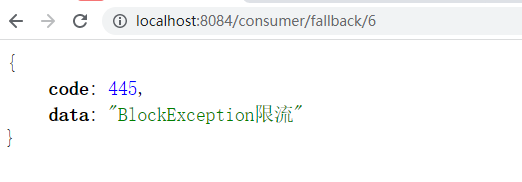
- 但是一旦触发熔断规则就变成了blockHandler来处理
exceptionsToIgnore属性
exceptionsToIgnore(since 1.6.0):用于指定哪些异常被排除掉,不会计入异常统计中,也不会进入 fallback 逻辑中,而是会原样抛出。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| @RestController
@Slf4j
public class DemoController {
@Value("${service-url.nacos-user-service}")
private String SERVICE_URL;
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@GetMapping("/consumer/fallback/{id}")
@SentinelResource(value = "falllback",fallback = "fallbackHandler",blockHandler = "blockHandler",
exceptionsToIgnore = {NullPointerException.class})
public JsonResult<String> fallback(@PathVariable Long id){
if(id<=3){
JsonResult<String> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL+"/info/"+id,JsonResult.class);
System.err.println(result.getData());
return result;
}else{
throw new NullPointerException("没有对应的数据记录");
}
}
public JsonResult<String> fallbackHandler(Long id,Throwable e){
JsonResult<String> result = new JsonResult<>(444,"NullPointerException异常");
return result;
}
public JsonResult<String> blockHandler(Long id, BlockException e){
JsonResult<String> result = new JsonResult<>(445,"BlockException限流");
return result;
}
}
|




